It’s February so that means it’s Black History Month. I think I will make this an annual thing, where I look at the “Father of Black History” Carter G. Woodson. He picked a week in February for Black History Week, then that week turned into a month and ta-da we are in Black History Month.

Dr. Carter G. Woodson (PhD, Harvard, 1912) noticed there was a lack of history documenting and telling the story of Black Americans in America. So he saw a problem and then fixed it. Quoting the NPS biography of Dr. Woodson, “The public knew very little about the role of African Americans in American history, and schools were not including African American history in their curriculum. He worked tirelessly throughout his life to remedy this problem, becoming nationally recognized as “the Father of Black History.” ” 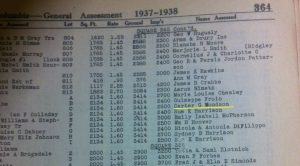
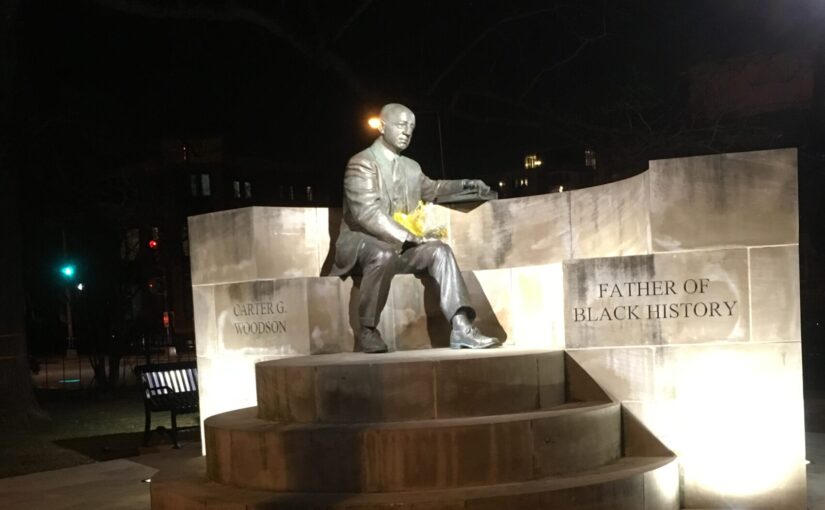
Dr. Woodson lived and worked at 1538 9th Street NW, which is in Shaw. This would explain the statue, if you missed it, at 9th and Rhode Island Avenue NW. And the National Park Service historic house.
To celebrate the month I had pondered the idea of looking at his 1912 book The History of the Negro Church, because last year I did a deep dive of his Mis-Education of the Negro. There are some problems. For one the first book I ordered had type so small I could not read it. When I did order a book these older eyes could read, I discovered the book was very boring. I have discovered that The History of the Negro Church is in the public domain (yay), on the Project Gutenberg site and may have the Kindle read it to me. I seriously looked at Fivver for audiobook narrators. On the other hand I could just wait for the next round of DC Humanities grants and have them chip in for an audiobook production of Woodson’s public domain works. Feel free to steal this idea.
Instead this year, I’ll do one chapter or more chapters (not the whole book) of The History of the Negro Church, a second review of Mis-Education, other Dr. Woodson related posts and a Truxton Circle related African American history book that was pretty good. I may do a few WSIC posts and one or two 1930 Black Home Owners of Truxton Circle.




 William Saunders was a TC resident, and he has a
William Saunders was a TC resident, and he has a